Publish a New Post in WP
These are the steps to create a post within your own externally hosted WordPress site. For help with sites hosted on WordPress.com please use these steps. Otherwise follow the steps below.
Quick Publishing
- Login to your WordPress Admin, and look for Posts > Add new.
- Fill in the blanks: enter a post title, body content
- Assign a category, add tags
- Add an excerpt (a brief summary shown on landing pages)
- Add a featured image (this is likely to make your post thumbnail, for your home and landing pages)
- Preview or Publish your post. Publishing your post will add it to your website.
Set your Screen Options
If I mention an option you can’t find, it’s likely hidden and needs to be enabled in screen options. In the top right of your screen you’ll find a hanging tab called screen options. Here you can show and hide options like; excerpt, comments and revisions.
As you get used to writing posts, you’ll hide options that you don’t need regularly to reduce clutter.
Descriptions of Post Fields
Title – The title of your post. A phrase that sums up the post and is likely to be searched for.
Permalink – The user friendly URL of your post. WordPress will convert your post title into a URL with hyphens. Its best to clear your permalink and to let WP recreate it if you change your title. Permalinks shouldn’t be too long, with WP removing less significant words in your URL. Permalinks settings can be altered within Settings > Permalinks.
Categories – Your site will have around 7-10 common categories to group your content. As I create WordPress and Magento websites, tips, tutorials and error fixing posts will go in their respective WordPress and Magento categories. Topics that are less common, and not central to your site are better grouped with tags.
Tags – Tags are the keywords you might assign to each post. Unlike categories which have subcategories, tags have no hierarchy. Tags form an additional way of grouping content and navigating around a site. If you wrote a post about attending an event, the event name and location, are most likely to be added as tags.
Excerpt – A brief teaser or summary of your post, that is displayed (depending on your theme) on your home, category, archives and search pages. The excerpt will usually accompany the post title, thumbnail and date.
Post Content
Adding content to a post is very similar to creating a MS Word document. Although you should try not to add anything in the way of colour or font styles, underlines or html. Instead you should let your theme’s CSS style your content, so your posts have a uniform look across the site.
Paragraph Text -To make your post easier to read you should break your post content into paragraphs. This text can then have links to other posts and pages on your site (such as your contact page) or to external content on other websites. When adding links make sure to add a title, to give an indication of what the page you’re linking to is about.
Headings – Sectioning your site with headings, makes the post easier to understand and will improve its SEO ranking. H3 headings are most commonly used within content, with H1 (most important) usually set automatically to the post’s title.
Images – Post Images should be optimised and set at less than 50kb. This is a large enough file size to prevent distortion, whilst making the image quick enough to load. Photography images should always be saved as jpegs. WordPress themes normally use a selection of image sizes across the site, which are resized from the featured image. To find the correct image dimensions, copy them from an earlier post, or ask your web developer who can find the thumbnails sizes set in your theme. Image files should also have a useful name, such as wordpress-create-post.jpg, not 0001.jpg. When embedding an image within the content using Add Media, make sure you have renamed the image before you upload it and give it an alt tag to describe the image. This alternative description is useful for people who may have difficulty viewing your image and again for SEO.
Gravatar / Author Photo
When you first publish a blog post or add a comment, a default grey image might be displayed as you don’t have a profile image assigned. By following this article, you can choose a gravatar image that will automatically be added to your account.
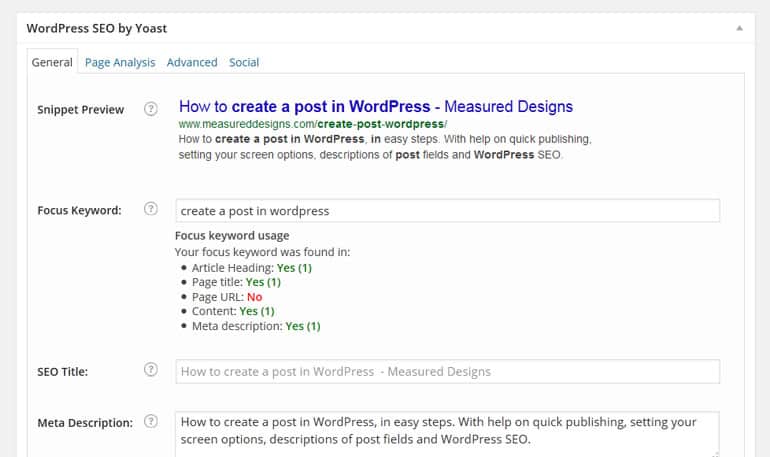
WordPress Post SEO
WordPress SEO by Yoast, will give you real time SEO feedback on your post. Add a focus keyword, or phrase and the SEO plugin will give you tips on how to make your content and meta data more SEO friendly.
WordPress Posts vs Pages
Now we’ve looked into how to create a post in WordPress, here’s a quick reminder of what a post actually is.
WordPress Posts
Posts are bits of content that make up your blog. They’re associated with a date and will usually be listed in reverse chronological order on your site, so the newest content surfaces at the top.
This is an example of a WordPress post.
For most simple sites a post will be an article, with images, text and links. As you’re likely to have many posts with similar content over time, WordPress posts can be grouped into categories and tag groups. You can also add comments to a posts.
WordPress Pages
Pages are static, with your About Us or Terms sections obvious examples of pages.
This is an example of a WordPress page.
These pages aren’t listed by date and won’t be grouped into categories or by tags. The core areas of your site, such as your homepage and blog/news landing page will also be pages. Pages will form the backbone of your site, populated by blog post content.
Take a look at our WordPress portfolio for clients based all over Essex, London and Norfolk. We’d love to help you get a website, you can be proud off.




